Skin Type
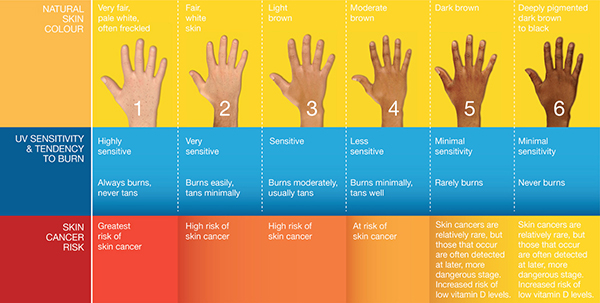
Skin phototype is determined genetically, and is one predictor of sensitivity to UV light and your risk of getting skin cancer. This classification was originally devised by the late Thomas Fitzpatrick, the professor of Dermatology at Harvard University. Lighter skin type is associated with higher sensitivity to UV and a higher risk of developing skin cancer. Type I is the lightest and Type VI is the darkest.
Type I
Skin is ivory white, you always burn easily, but never tan in the sun. Your skin is extremely susceptible to sun damage as well as all skin cancers. You should always follow sun protections measures and seek the shade whenever you are out in the sun. Use sunprotective clothing and a daily facial sunscreen with an SPF of 30+. Check your skin from head-to-toe on a regular basis, at least every 3 months, paying careful attention to any new or suspicious growths, and ensure you have an annual skin examination by your doctor.
Type II
Skin is white, you almost always burn easily, and tan minimally with difficulty. You are highly susceptible to sun damage on the skin as well as all skin cancers. You should always follow sun protections measures and seek the shade whenever you are out in the sun. Use sunprotective clothing and a daily facial sunscreen with an SPF of 30+. Check your skin from head-to-toe on a regular basis, at least every 3 months, paying careful attention to any new or suspicious growths, and ensure you have an annual skin examination by your doctor.
Type III
Skin is beige or olive brown, you burn moderately, and your skin will tan moderately to a light brown. You are susceptible to sun damage on the skin as well as all cancers. You should always follow sun protections measures and seek the shade whenever you are out in the sun. Use sunprotective clothing and a daily facial sunscreen with an SPF of 30+. Check your skin from head-to-toe on a regular basis, at least every 3 months, paying careful attention to any new or suspicious growths, and ensure you have an annual skin examination by your doctor.
Type IV
Skin is light brown, you burn minimally and you tend to tan moderately to a medium brown. You are still at some risk of sun damage to the skin and the development of skin cancers, particularly if you are an outdoor worker or you obtain a lot of leisure time sun exposure. Use sunprotective clothing and a daily facial sunscreen with an SPF of 30+ You should always follow sun protections measures and seek the shade whenever you are out in the sun. Check your skin from head-to-toe on a regular basis, at least every 3 months, paying careful attention to any new or suspicious growths, and ensure you have an annual skin examination by your doctor.
Type V
Skin is always brown, you rarely burn and can tan profusely to dark brown. You still have a small risk for developing skin cancer. Use sunprotective clothing and a sunscreen with an SPF of 30+ and seek the shade between 11 AM and 3 PM. Acral lentiginous melanoma, an aggressive form of melanoma, is more common in people with darker skin type. These melanomas tend to appear under the finger or toenails. Check your skin from head-to-toe on a regular basis, every 3 months, paying careful attention to any new or suspicious growths. See your doctor if there are any suspicious growths, especially if they are on the palms, soles of the feet or inside the mouth.
Type VI
Skin is always dark brown, you do not burn, and tan profusely. You still have a small risk for developing skin cancer. Use sun protective clothing and a sunscreen with an SPF of 30+ and seek the shade between 11 AM and 3 PM. Acral lentiginous melanoma, an aggressive form of melanoma, is more common in people with darker skin type. These melanomas tend to appear under the finger or toenails. Check your skin from head-to-toe on a regular basis, every 3 months, paying careful attention to any new or suspicious growths. See your doctor if there are any suspicious growths, especially if they are on the palms, soles of the feet or inside the mouth.